Many teams tend to compromise their decisions for the sake of consensus, harmony, and “esprit de corps.” The result is often a lowest-common-denominator decision upon which everybody in the team agrees. This predisposition for a team to minimize conflict and value conformity is the psychological phenomenon of Groupthink.
.jpg) In the 1970s, American psychologist Irving Janis defined Groupthink as “a mode of thinking that people engage in when deeply involved in a cohesive in-group, when the members’ strivings for unanimity override their motivation to realistically appraise alternative courses of action.” Janis argued that Groupthink “undermines critical analysis, legitimizes ignorance, reinforces collective biases, and promotes a group self-image of infallibility.”
In the 1970s, American psychologist Irving Janis defined Groupthink as “a mode of thinking that people engage in when deeply involved in a cohesive in-group, when the members’ strivings for unanimity override their motivation to realistically appraise alternative courses of action.” Janis argued that Groupthink “undermines critical analysis, legitimizes ignorance, reinforces collective biases, and promotes a group self-image of infallibility.”
Negative Effects of Groupthink in Teamwork
Teams are prone to Groupthink and a variety of other detrimental decision-making approaches, but are seldom aware of it.
- Groupthink suppresses dissent Individuals resign to group pressure, thereby conforming their opinions to a decision that they believe will achieve consensus. Groupthink discourages dissenters from “rocking the boat.” Over time, nonconformists are gradually shunted aside or excluded from the team altogether.
- Groupthink engenders self-censorship. Individuals who disagree with the chosen course of action remain silent because they reason they cannot change others’ minds. Consequently, the team tends to focus its discussions on ideas that everyone agrees about rather than ideas that everyone disagrees about.
- Groupthink gives team members greater confidence in their collective decisions than their individual decisions. Therefore, Groupthink leads individuals to publicly endorse ideas and decisions that they view as common for the group, even if they personally have reservations about them.
- Groupthink stifles creativity and independent thinking. When individuals are unwilling to bring up and confront difficult issues, the team fails to examine alternative viewpoints that could be contentious. This leads to irrational and flawed decisions.
Antidote to Groupthink in Teamwork
An awareness of Groupthink and other group dynamic biases combined with some hands-on intervention, self-reflection, and control can help teams make better decisions.
- Create an organizational environment where individuals can freely voice their ideas, challenges, and concerns. Individuals must feel comfortable with taking interpersonal risks, admitting hesitations, and challenging one-another. Absent an inclination to avoid conflict, a team can easily discuss and debate different perspectives.
- Think about the right information required to make sound decisions. Consider the strongest counter-argument to every idea.
- Do not suppress disagreements or dominate the dissenters. Carefully examine the reasons and implications of alternate viewpoints.
- Divide a team into sub-teams or partnerships and set each sub-team to work on a problem independently. Encourage them to take into account the plusses and the minuses of each idea.
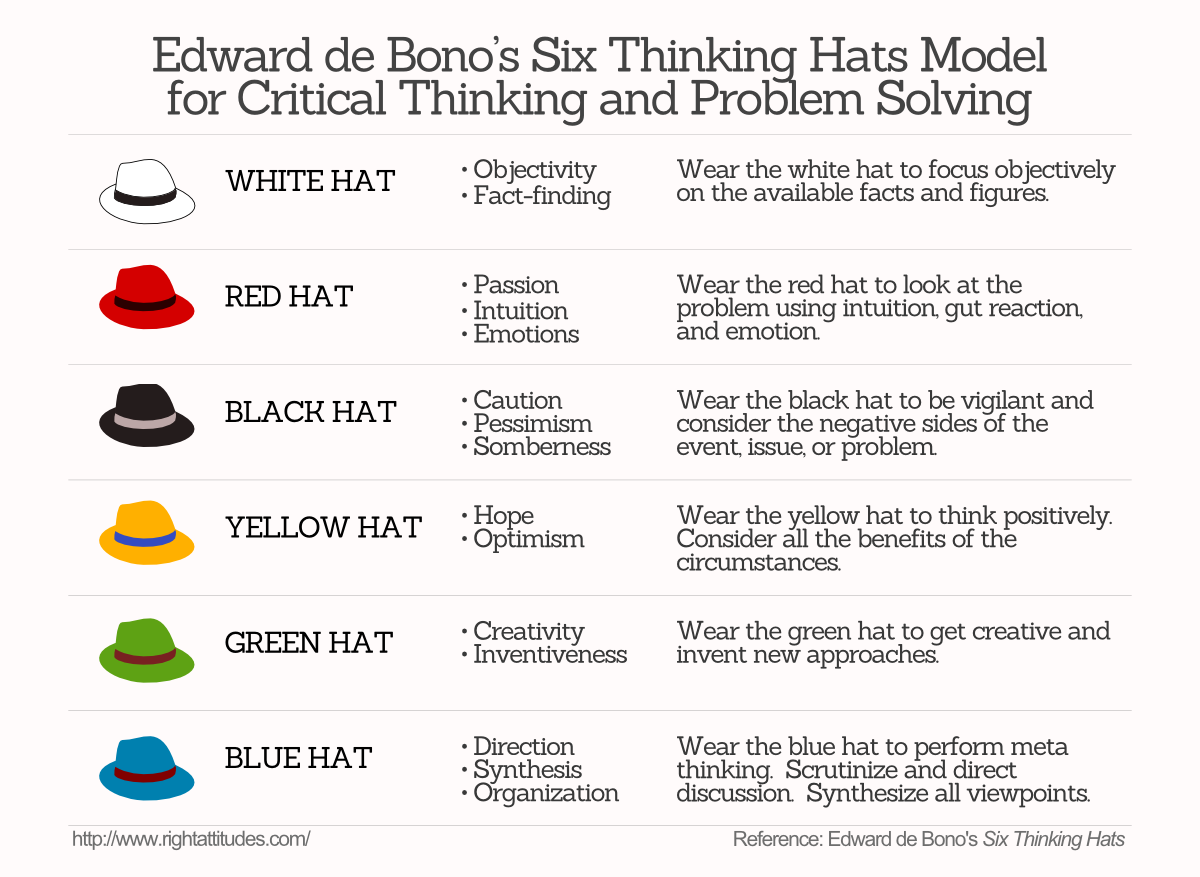
- Designate one team member as a devil’s advocate to argue enthusiastically against all contemplated ideas. This can force the team to discuss and debate the concomitant merits and demerits of different ideas. In Edward De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats process (see my book summary), the devil’s advocate wears the “black hat.”
- Invite outside consultants and subject-matter experts to discuss key issues and review decisions.
- Appoint a moderator who can engage the team collectively and individually by gathering all points of view, giving feedback, and challenging the team’s thinking. Ideally, the moderator should be an independent third party who can be comprehensive and forthright.
- Step back regularly from the team’s deliberation process to reflect on the effectiveness of the team’s decision-making and intervene where necessary. In the Six Thinking Hats process, De Bono suggests adding reflection time at the end of each meeting to analyze the process’ effectiveness.
Idea for Impact: Sometimes, Teamwork is Overrated
Don’t get me wrong: teamwork can be very powerful, but only when teams consist of individuals who have the right expertise and who are willing to voice their forthright opinions, dissent, and build consensus. Avoid teamwork when one person or a partnership with complementary skills and styles may achieve identical objectives.
To prevent Groupthink, establish an environment where speaking up is encouraged and rewarded. Welcome disagreements, avoid dominating dissenters, and contemplate the strongest counter-argument to every idea.

.jpg)
 Meet the offending employee discretely and ask, “Aaron, are you aware of our dress code?” Then, mention the specific instance of the problem, “Some of your clothes are a bit more provocative than appropriate for our workplace.” State facts and not judgments. Relate any rebuke to a business purpose, viz., the need for a professional workplace or dress-appropriateness in customer-facing roles. Ask the employee how he/she could rectify the matter. If necessary, remind that employees must accommodate the employer, not the other way around.
Meet the offending employee discretely and ask, “Aaron, are you aware of our dress code?” Then, mention the specific instance of the problem, “Some of your clothes are a bit more provocative than appropriate for our workplace.” State facts and not judgments. Relate any rebuke to a business purpose, viz., the need for a professional workplace or dress-appropriateness in customer-facing roles. Ask the employee how he/she could rectify the matter. If necessary, remind that employees must accommodate the employer, not the other way around.