One of the reasons many people are not as productive as they want to be is not because they haven’t found the right ideas that can help them take charge of their lives.
They can’t be productive because they keep looking for “better” ideas instead of settling on a “good enough” idea and then putting it into rigorous practice.
Looking for the Best Can Be Counterproductive
This is comparable to weight-loss programs. People buy more and more books on dieting, but don’t lose weight by merely buying diet books. It’s easier to buy books than it is to go on a diet. Recognizing that most diet plans boil down to basic strategies—eat more fruits and veggies, keep portions under control, and stay physically active—and implementing these simple ideas purposely could be as effective a diet program as any out there.
Look, no productivity tool can fit all your requirements. The inadequacies of any productivity system you try out will drive you towards looking for a different tool. But this quest to define the best never ends.
Idea for Impact: Never underestimate the power of a simple idea that is well executed.
If you can identify a simple system and implement its key principles with discipline, you may not need the “best” system.
As Charlie Munger has stated in describing the simplicity of Warren Buffett’s philosophy at Berkshire Hathaway, “Our ideas are so simple that people keep asking us for mysteries when all we have are the most elementary ideas.”
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
 Here are our most popular exclusive features of 2018. Pass this on to your friends; if they like these, they can sign up to receive our
Here are our most popular exclusive features of 2018. Pass this on to your friends; if they like these, they can sign up to receive our  Many people claim that they
Many people claim that they 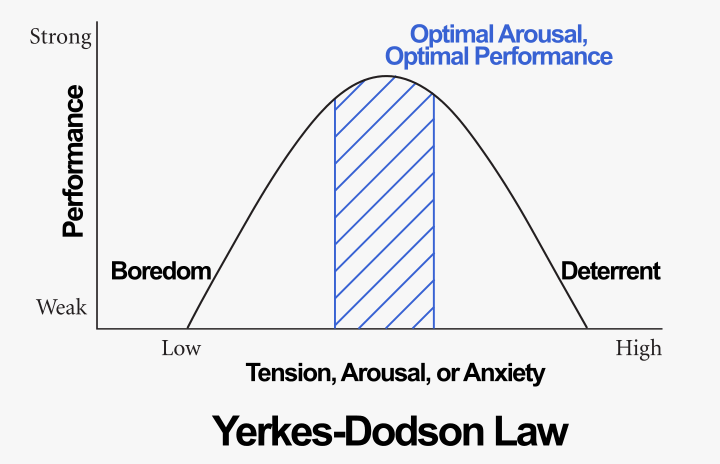
 Seek fresh eyes. Ask new employees and interns to make a note of every question they have about how things get done in your organization. If anything—reports, approvals, meetings, reviews—doesn’t seem sensible, let them record those inefficiencies. After a few weeks, when they’ve become familiar with the organization and its workflow, have them reassess and report their observations. The best improvement ideas come from people who
Seek fresh eyes. Ask new employees and interns to make a note of every question they have about how things get done in your organization. If anything—reports, approvals, meetings, reviews—doesn’t seem sensible, let them record those inefficiencies. After a few weeks, when they’ve become familiar with the organization and its workflow, have them reassess and report their observations. The best improvement ideas come from people who  Part three covers the particular nuances of reading various types of literature: practical books, creative literature, stories, plays, poems, history, philosophy, science, mathematics, and social science.
Part three covers the particular nuances of reading various types of literature: practical books, creative literature, stories, plays, poems, history, philosophy, science, mathematics, and social science.