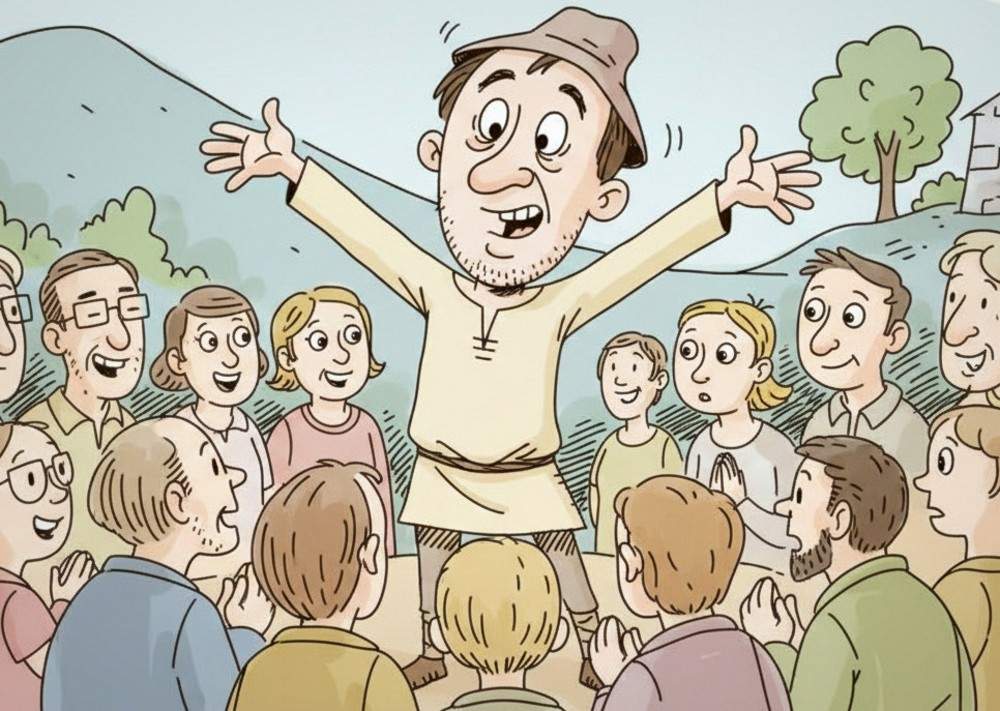

One of my favorite films is Rashomon (1950,) Akira Kurosawa’s masterpiece that gave psychology the term “The Rashomon Effect.” The film is famous for its structure: a single crime retold from multiple perspectives, each account contradicting the others. What emerges is not clarity but confusion, a reminder that memory, perception, and self-interest distort the truth. At its core, Rashomon is about unreliable narrators—characters whose versions of events are shaped as much by omission and self-deception as by fact.
Unreliable narrators transform messy realities into tidy, persuasive accounts. They smooth contradictions, omit inconvenient details, and present one interpretation as if it were the only truth. The result is a polished narrative that feels complete—even while concealing fractures.
This theme is hardly confined to Rashomon. Unreliable narrators and neat tales recur across cinema: Forrest Gump (1994,) The Usual Suspects (1995,) Fight Club (1999,) American Psycho (2000,) and Joker (2019) all show how fallible narrators can manufacture coherence and persuade audiences to accept a deceptively seamless version of events.
The problem lies in compromised credibility. Unreliability stems from self-deception, deliberate deceit, mental instability, or selective omission. These aren’t just stylistic quirks—they reshape the relationship between what is told and what actually happened. A neat narrative is rarely neutral; it reflects choices about emphasis and omission. Recognizing that neatness often signals construction is the first step toward resisting the illusion of completeness.
When a story feels too tidy, treat that neatness as a warning sign. Assume something is missing. Look for gaps in chronology, absent witnesses, sudden shifts in focus, or conveniently omitted facts. Silence itself can be evidence, and corroboration or alternative perspectives can turn absence into insight. Here’s how to read against the grain:
- Treat neatness as a warning sign. If a story feels too tidy, assume missing information matters. Gaps in chronology, absent witnesses, sudden shifts in focus, or conveniently omitted facts all carry meaning. Seek corroboration, alternative timelines, and outside perspectives to turn silence into evidence.
- Use inconsistencies as diagnostic tools. Contradictions reveal pressure points. Shifting memories, mismatched timelines, or actions that contradict stated motives expose where the constructed story begins to unravel.
- Assess incentives behind the polish. Every narrator has stakes—reputation, sympathy, control, or self-preservation. Those stakes shape which facts are highlighted and which are buried. Read emphasis and omission as strategic choices, and weigh what the narrator gains from presenting a clean version.
These habits of skepticism apply well beyond film criticism. Separate observation from interpretation, test for internal consistency, and consider incentives before accepting a neat account. This approach does not guarantee certainty, but it replaces passive acceptance with disciplined questioning.
Idea for Impact: The neat story is often the most dishonest. Truth is ragged, and only a fool mistakes tidiness for accuracy. Beware the narrator who makes it all add up.
 A lie is rarely noble. A truth without tact is often cruelty dressed up as virtue.
A lie is rarely noble. A truth without tact is often cruelty dressed up as virtue. My friend Jack recently offered a retrospective on his decade-long dalliance with sneaker trends—a ride as unpredictable as it was swift. He began faithfully attached to New Balance, those once-maligned “dad shoes” that screamed suburban resignation. Then came Converse, adopted not for comfort but for credibility, as his children entered the age of judgment and he entered the age of trying not to embarrass them. Shortly thereafter, he flirted with On sneakers during a Lululemon-inspired phase that boldly declared, “I’m trendy, indeed!” Yet as fashion’s fickle currents swept him toward HOKA’s cloud-like comforts, Jack eventually circled back to a reinvented New Balance—now celebrated as a bona fide streetwear icon. Worn out by the relentless trend chase, he
My friend Jack recently offered a retrospective on his decade-long dalliance with sneaker trends—a ride as unpredictable as it was swift. He began faithfully attached to New Balance, those once-maligned “dad shoes” that screamed suburban resignation. Then came Converse, adopted not for comfort but for credibility, as his children entered the age of judgment and he entered the age of trying not to embarrass them. Shortly thereafter, he flirted with On sneakers during a Lululemon-inspired phase that boldly declared, “I’m trendy, indeed!” Yet as fashion’s fickle currents swept him toward HOKA’s cloud-like comforts, Jack eventually circled back to a reinvented New Balance—now celebrated as a bona fide streetwear icon. Worn out by the relentless trend chase, he  Ryanair’s CEO Michael O’Leary has long been one of my most admired businessmen. His achievements speak for themselves, but what has always impressed me even more is the consistency of his communication and the clarity of the philosophy that underpins everything he does.
Ryanair’s CEO Michael O’Leary has long been one of my most admired businessmen. His achievements speak for themselves, but what has always impressed me even more is the consistency of his communication and the clarity of the philosophy that underpins everything he does.
 His flair for humorous controversy goes back years. During a 2001
His flair for humorous controversy goes back years. During a 2001  In 2023, a video of the Dalai Lama interacting with a young boy at a public event in India ignited
In 2023, a video of the Dalai Lama interacting with a young boy at a public event in India ignited  The new year marked
The new year marked  When Alan Mulally became Ford’s CEO in September 2006, the company was teetering on the
When Alan Mulally became Ford’s CEO in September 2006, the company was teetering on the  It’s a curious feature of our age that we still require, by law, ashtrays in the lavatories of commercial aircraft. Not because we’re nostalgic for the days when the skies were thick with the fug of unfiltered Marlboros, but because—despite decades of prohibition—someone, somewhere, will inevitably decide the rules
It’s a curious feature of our age that we still require, by law, ashtrays in the lavatories of commercial aircraft. Not because we’re nostalgic for the days when the skies were thick with the fug of unfiltered Marlboros, but because—despite decades of prohibition—someone, somewhere, will inevitably decide the rules  The
The